Ever since we knew how to harness energy from the sun to generate electricity we have been constantly trying to increase the efficiency of doing it and bifacial solar panels is another effort in doing that. In this article we will see what are bifacial solar panels?, how they work, advantages & disadvantages and when should you use them.
Bifacial solar panels are solar panels which have solar cells sandwiched between transparent glass. The average monofacial solar panel only generates electricity when sunlight strikes it from the front side whereas bifacial solar panels generate electricity from both there faces both front and back.
What are bifacial solar panels?
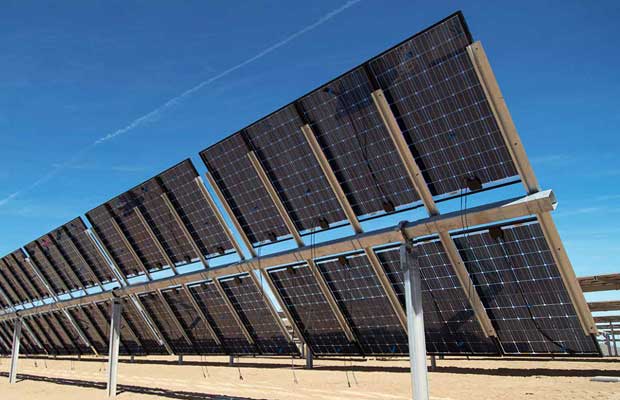

Even today the highest efficiency solar panels can only convert only 20% to 22% of the incident sunlight into useful electricity, the rest of it is wasted. This problem is solved by bifacial solar panels.
Unlike monocrystalline or polycrystalline solar panels which has white back sheet to support the solar cells, bifacial solar panels have a transparent glass on their back which allows the light to pass through the front of solar panel, hit the ground, reflect back from the ground and hit the solar cells again, this time from the back. Hence the solar cells are getting exposed to the sunlight even from the back thus, more generation.
Typically bifacial solar panels are made with polycrystalline or monocrystalline solar cells and are available in wattage ranging from 280 Watt to 450 Watt.
Bifacial module manufacturers have two primary ways of constructing a bifacial cell. Some encapsulate both sides of the cells in a layer of solar glass. Others use glass on the front and a transparent polymer-backsheet material on the back.
In almost all bifacial solar panels the junction box is positioned in a way that it does not cast any shadow on the solar cells.
How bifacial solar panels Work?
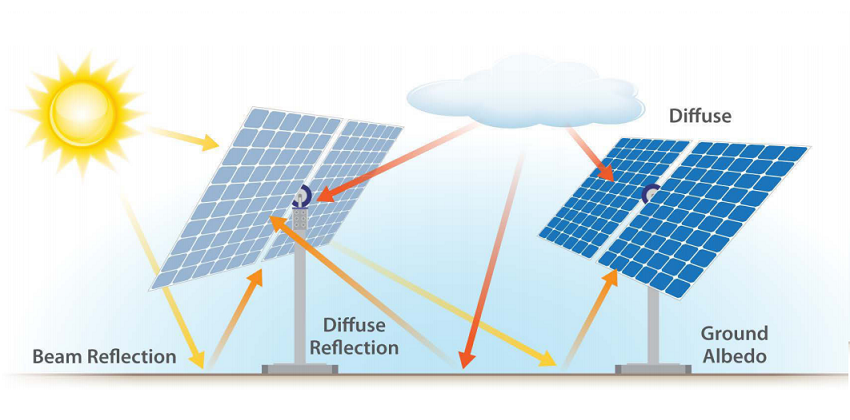
Bifacial solar panels generate electricity by the following steps.
- Sunlight is incident on the front on the solar panel, about 20% of it is converted to electricity and the rest 80% is either reflected, refracted, transmitted or absorbed.
- The light which gets transmitted through the solar cells hits the ground, gets reflected back and hits the solar cells again.
- Some light which directly hits the ground also gets reflected and hits the solar cells from the backs.
Hence in comparison with conventional solar panels more sunlight hits the solar cells thus, more generation.
Factors affecting bifacial solar panels generation:
The idea of bifacial solar panels seems good but there are a lot of factors that needs to be in place to see reasonable increase in generation. The factors affecting bifacial solar panels generation are.
- Module mounting height – The closer a bifacial PV array is to the ground or a roof surface, the less chance reflective light will reach the back of the array. A significant bifacial energy boost is possible, however, with a relatively modest height increase. In one simulation, the energy boost curve was steepest between 0 and 7.9 inches. After about 20 inches, the curve flattened out and additional energy gains were negligible. This data from SolarPro suggests that bifacial modules are appropriate for most ground-mounted applications, given that the leading edge of these arrays is usually from 18 inches to 36 inches above grade.
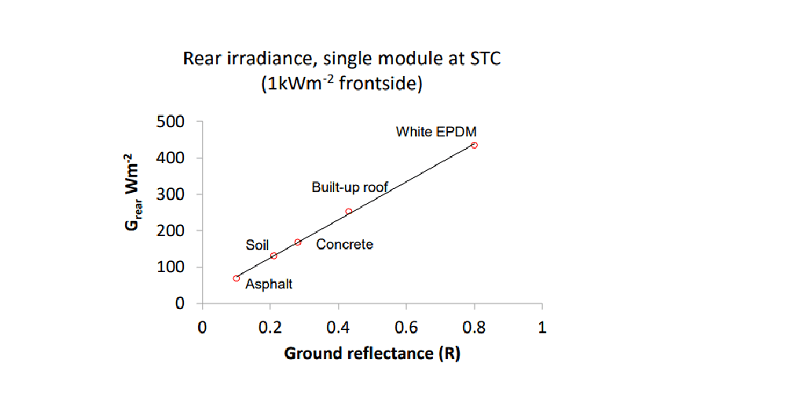
- Ground surface – Different surface reflect light to a different extent. In general a light colour surface reflects more light than a dark colour surface. For example a roof painted silver will reflect more sunlight than a roof painted black. From the below graph it is evident that if white EPDM membrane is more effective in reflecting the sunlight than asphalt.
Efficiency of bifacial solar panels:
All this reflection, refraction, double glass design is done to increase the solar panels generation, but how much more efficient is a bifacial solar panel from conventional monofacial solar panel? Let’s find out.
I have pulled the following data from Canadian Solar website, it is for CS3U-360PB-AG high efficiency BiKu module.
| Bifacial Gain(%) | Watt (W) | Efficiency (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0% | 360 W | 17.95% |
| 5% | 378 W | 18.85% |
| 10% | 396 W | 19.74% |
| 20% | 432 W | 21.54% |
| 30% | 468 W | 23.33% |
As you can see above that for 30% bifacial gain we get 5 % more efficiency.
This means if 1 kW of conventional solar panels each of 360 watt generates 100 kWh in a month then, 1 kW of the above BiKu panel each of 360 watt would generate at max 105 kWh in a month. This doesn’t sound much but for a solar power park with thousands of panel it is well worth.
NOTE:
- All test are done under Standard Test Conditions (STC) of irradiance of 1000 W/m2, spectrum AM 1.5 and cell temperature of 25°C.
- Bifacial Gain: The additional gain from the back side compared to the power of the front side at the standard test condition. It depends on mounting (structure, height, tilt angle etc.) and albedo of the ground.
For more details on efficiency you can check this case study from NREL
Cost of bifacial solar panels:
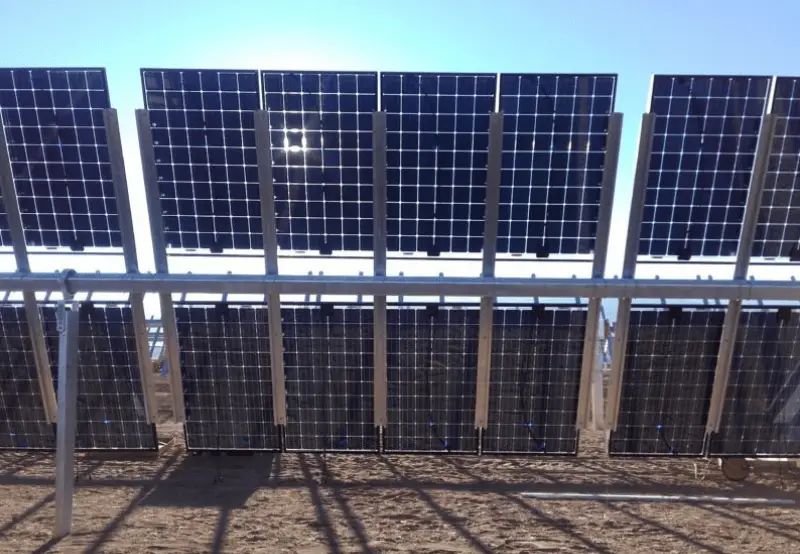

I live in India and here as of today bifacial solar panels are not much popular, hence I couldn’t get pricing for major brands. However I found pricing for LG NeON 2 LG385N2T-A5 BiFacial Solar Module, it is Rs 46 / Watt.
To give you an idea about cost comparison, conventional polycrystalline solar panel of same wattage as the above bifacial solar panel cost around Rs 20 / Watt to Rs 25 / Watt.
Hence you can see that bifacial solar panels are quite expensive and economically doesn’t work for small project.
The mounting structure which has to be used for bifacial solar panel is more expensive and requires experience solar installer this will also add to the overall cost of your solar system.
Where to use bifacial solar panels?
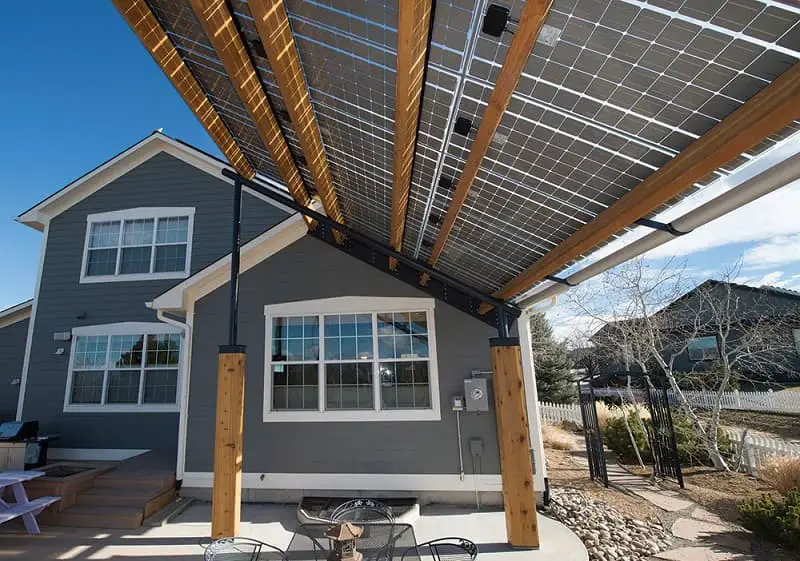

As we say above that for best generation your bifacial solar panels should be installed at elevated height and the surface underneath it should be reflective, So if your house has metal roof then you will need to use structure to elevate your solar panels to a good height so that good amount of light reflects back. If solar panels are installed directly on the roof you won’t see any increase in the generation.
Hence, ideally solar panels are good for ground mounted installations or on a flat roof where you can elevate your solar panels and change the surface below it to be more reflective.
In 2020, I would say it’s too early to use bifacial solar panels for residential application but they are being successfully used on several large scale for solar power parks and large utility scale projects.

Advantages of bifacial solar panels:
Bifacial solar modules offer some unique advantages over traditional solar panels:
- Better performance at similar project size, more production at a barely higher installation cost (for large scale project), so LCOE reduces.
- Synergy between rear-facing exposure and improved ventilation
- Bifacial PV panel are more aesthetically pleasing
- Unique ability to generate electricity from direct sunlight.
- Ability to produce electricity from reflective light that passes through those panels.
- Bifacial panels do not contain potential induced degradation.
- Most of the bifacial panels possess a warranty of almost 30 years, unlike the usual 25-year warranty that comes with the traditional solar panels.
- Glass in the bifacial panels aid in preventing threats associated with UV exposure and moisture permeability.
- Due to the high strength of glass, the modules are safe from chemical corrosion.
- The bifacial solar panels lack aluminum frames. Therefore, they don’t need grounding. It aids in saving material as well as time during the installation process.
Disadvantages of bifacial solar panels:
Bifacial solar panels has many disadvantages over traditional solar panels:
- Generally high installation cost.
- Bifacial solar panels cannot be employed during the night, a cloudy day, or during a storm.
Conclusion:
Bifacial solar panel is promising technology and can help to produce more power in same amount of area.
However they should be used in more and more large scale utility project to instill confidence in the average solar installer to use it in their projects as well.
If you liked this article then feel free to share it on WhatsApp, Facebook, Pinterest, Reddit.
Please share your views in the comments section.
Thank You 🙂





